Cómo encender un LED en la placa Arduino UNO usando el lenguaje de programación Python y la clase pyFirmata, que a su vez usa el protocolo Firmata para comunicarse con microcontroladores. Realizaremos la conexión con el microcontrolador Arduino UNO por puerto USB desde un equipo informático con Windows 10.
- Un poco de teoría Firmata Python pyFirmata.
- Requisitos para desarrollar proyecto de conexión de PC con placa Arduino por USB con Python.
- Código Python para conectar con placa Arduino mediante USB y encender un LED.
- Anexo.
Un poco de teoría Firmata Python pyFirmata
Firmata
Firmata es un protocolo para comunicarse con microcontroladores desde un software en un PC (o también desde un teléfono inteligente, tableta, etc.). El protocolo se puede implementar en el firmware de cualquier arquitectura de microcontrolador, así como en cualquier paquete de software de PC.
Firmata se basa en el formato de mensaje MIDI en el que los bytes de los comandos son de 8 bits y los bytes de datos son de 7 bits.
En teoría, el protocolo Firmata podría implementarse para cualquier plataforma de microcontroladores. Sin embargo, actualmente la implementación más completa es para Arduino (incluidos los microcontroladores compatibles con Arduino).
Python
Usaremos como lenguaje de programación Python. Podemos escribir el código Python directamente en un editor de texto plano o bien usar un IDE, que nos ayudará en el proceso de compilación y depuración. En el siguiente enlace mostramos cómo instalar Python en Windows y cómo instalar y usar un IDE de desarrollo para Python:
pyFirmata
pyFirmata es una interfaz de Python para el protocolo Firmata. Será esta interfaz la que usemos para la conexión con Arduino desde nuestro equipo a través del puerto USB.
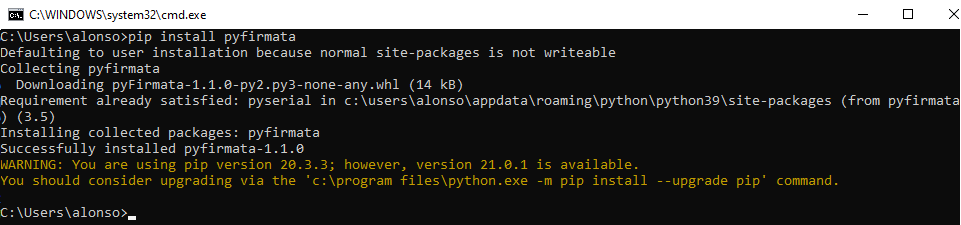
Para instalar esta interfaz en Python, una vez instalado, como indicamos en este artículo, abriremos una ventana de MS-DOS (para el caso de equipos Windows) y ejecutaremos el siguiente comando:
pip intall pyfirmata
Si todo es correcto nos indicará que el paquete pyfirmata se ha instalado correctamente, con el mensaje:
Installing collected packages: pyfirmata
Successfully installed pyfirmata-1.1.0
Requisitos para desarrollar proyecto de conexión de PC con placa Arduino por USB con Python
Para realizar este proyecto Python de ejemplo de conexión a un microcontrolador Arduino UNO mediante el puerto USB de un equipo. Como ejemplo de prueba de conexión encenderemos un LED conectado a Arduino. A continuación indicamos lo que necesitaremos.
Equipo informático, placa Arduino UNO, LED
Necesitaremos un equipo informático (puede ser con sistema operativo Windows, Linux o MAC OS). En nuestro caso usaremos un equipo con Windows 10.
También necesitaremos, obviamente, una placa Arduino UNO, como esta:
Con su cable USB de tipo A-B para la conexión de la placa Arduino con PC:
Un LED, aunque no es necesario para este proyecto, dado que la placa Arduino UNO incluye un LED integrado para el PIN 13. Aún así, si disponemos del LED, será más vistoso:
Si hemos optado por adquirir el LED, lo conectaremos a la placa Arduino. La patilla larga, el ánodo irá insertado en el PIN 13 y la corta en el PIN GND:
IDE de desarrollo Arduino
Para preparar Arduino UNO para que interactúe con el equipo informático a través del puerto USB, tendremos que transferirle un programa firmata a Arduino. Para ello usaremos el IDE de desarrollo propio de Arduino, que está disponible de forma gratuita en su web oficial.
Descargaremos el IDE de desarrollo de Arduino para el sistema operativo que estemos usando, las posibilidades son Windows, Linux, Mac OS X y sistemas con ARM, tanto en 32 bits como en 64 bits.
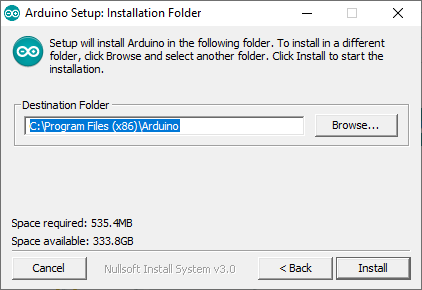
Descargaremos e instalaremos Arduino IDE, el proceso es muy sencillo. Seguiremos los pasos del asistente:
Elegiremos la carpeta de instalación:
Iremos aceptando todos los mensajes de instalar los drivers, para el puerto COM:
El USB Driver SRL:
El USB Driver LLC:
Conexión placa Arduino UNO a USB del equipo
Conectaremos la placa Arduino al equipo, para ello conectaremos el cable USB al conector de la placa Arduino:
Y conectaremos el otro extremo del cable a un puerto USB del equipo informático:
Cargar programa firmata y enviar a placa Arduino UNO
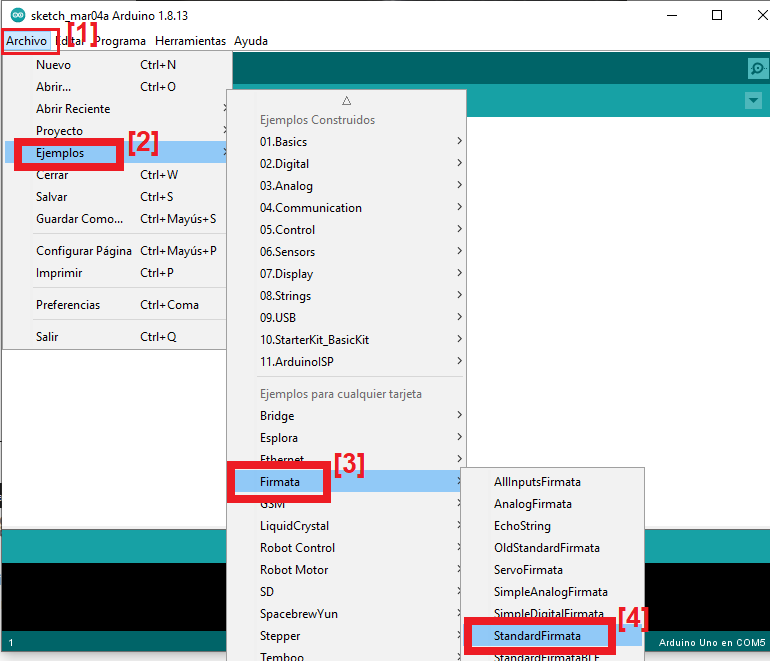
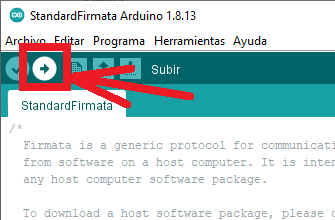
El siguiente paso, una vez instalado el IDE Arduino y conectada la placa Arduino al equipo por USB, será cargarle el programa firmata. Para ello abriremos el IDE Arduino y pulsaremos en el menú «Archivo» [1] – «Ejemplos» [2] – «Firmata» [3]- «StandardFirmata» [4]:
Nota: en el anexo incluimos el código Arduino de Firmata (StandardFirmata) que le pasamos al microcontrolador Arduino.
Una vez cargado el código lo enviaremos a la placa Arduino. Antes de enviarlo nos aseguraremos de que tenemos correctamente configurado el puerto en el Arduino IDE, en el menú «Herramientas» – «Puerto: «COMX (Arduino Uno)» – «COMX (Arduino Uno)». Elegiremos el puerto COM virtual emulado desde el USB, guardaremos este número de puerto, que posteriormente necesitaremos conocer para la aplicación Python:
Ahora podremos subir y cargar el programa en la placa Arduino, para ello pulsaremos en el botón «Subir»:
Esperaremos a que suba el programa, suele tardar unos segundos. Si todo es correcto mostrará en la parte inferior «Subido». Si hay algún error nos lo indicará.
A partir de ahora tendremos preparada la placa Arduino UNO para la comunicación mediante el puerto USB del equipo con firmata.
Código Python para conectar con placa Arduino mediante USB y encender un LED
A continuación mostramos el código fuente en Python para conectar con la placa Arduino a través del USB del equipo. El ejemplo encenderá y apagará un LED continuamente hasta que no se interrumpa el programa o se desconecte la Placa Arduino:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
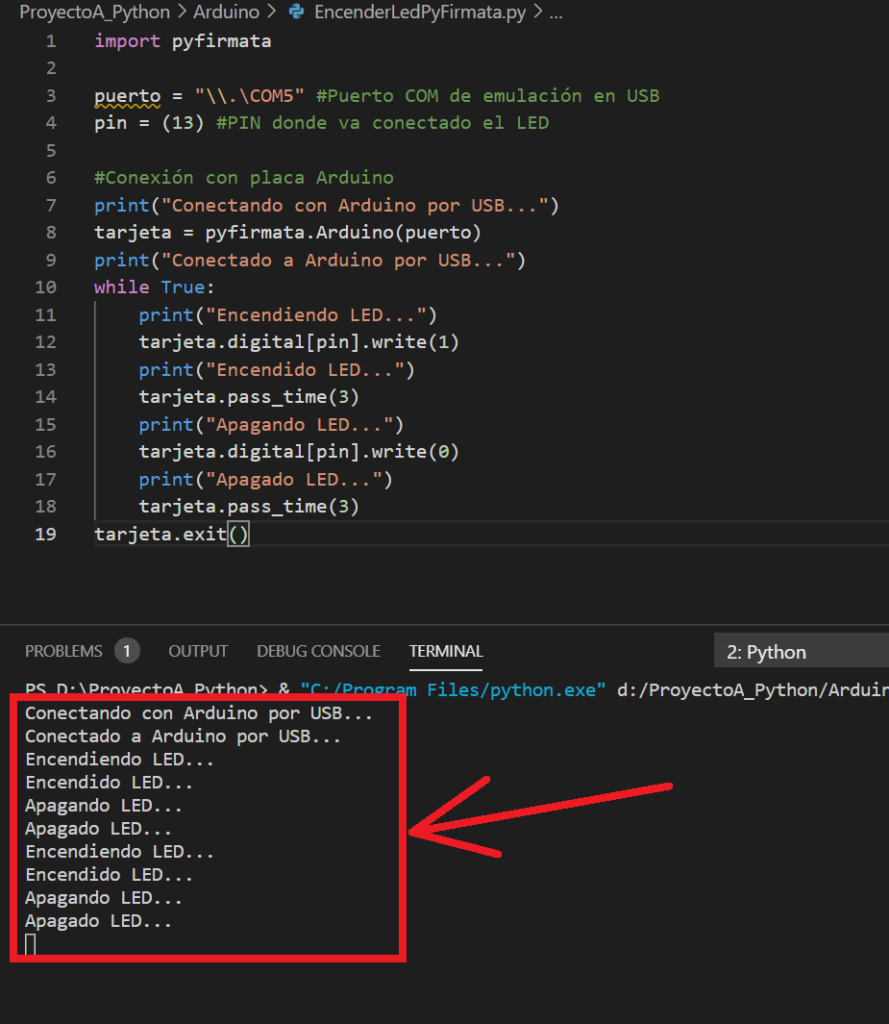
import pyfirmata puerto = "\\.\COM5" #Puerto COM de emulación en USB pin = (13) #PIN donde va conectado el LED #Conexión con placa Arduino print("Conectando con Arduino por USB...") tarjeta = pyfirmata.Arduino(puerto) print("Conectado a Arduino por USB...") while True: print("Encendiendo LED...") tarjeta.digital[pin].write(1) print("Encendido LED...") tarjeta.pass_time(3) print("Apagando LED...") tarjeta.digital[pin].write(0) print("Apagado LED...") tarjeta.pass_time(3) tarjeta.exit() |
Como vemos, el código anterior usa la librería pyfirmata, y el puerto virtual COM5. Habrá que cambiarlo por el correspondiente. Realizará la conexión con Arduino y ejecutará un bucle para encender el LED, esperar 3 segundos, apagarlo, esperar otros 3 segundos y voler a repetir el proceso. Y así sucesivamente mientras no se interrumpa el programa o se desconecte la placa. El programa en funcionamiento:
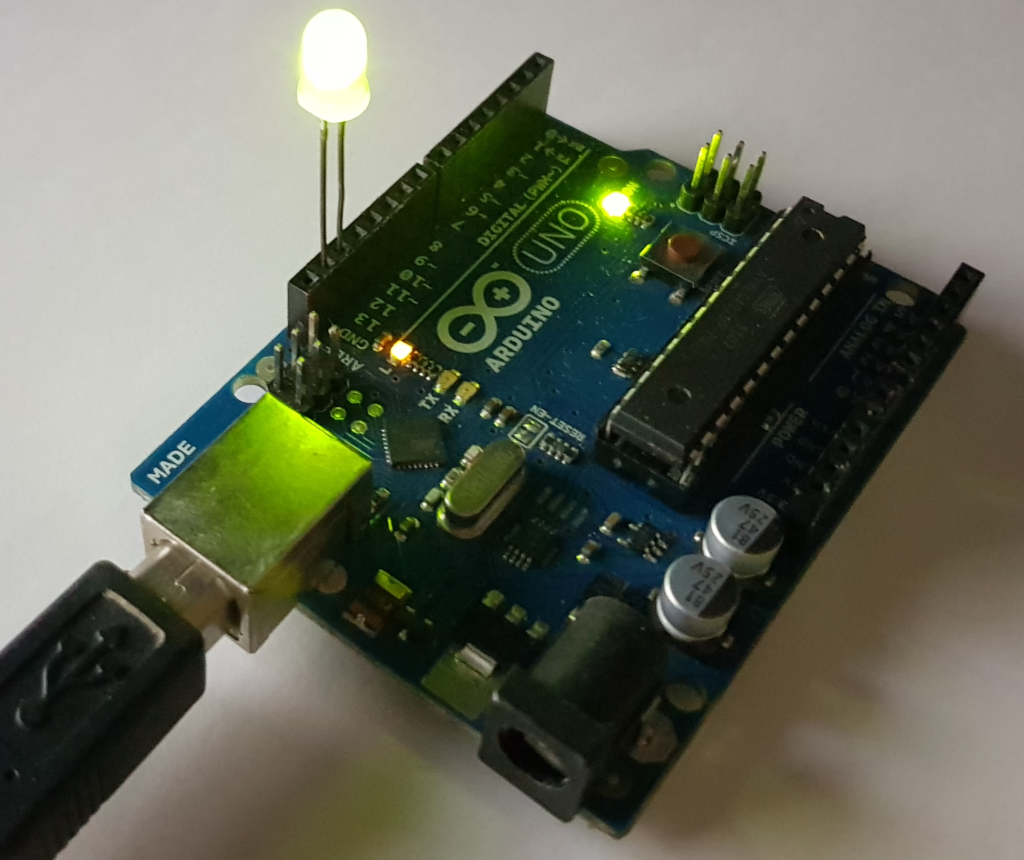
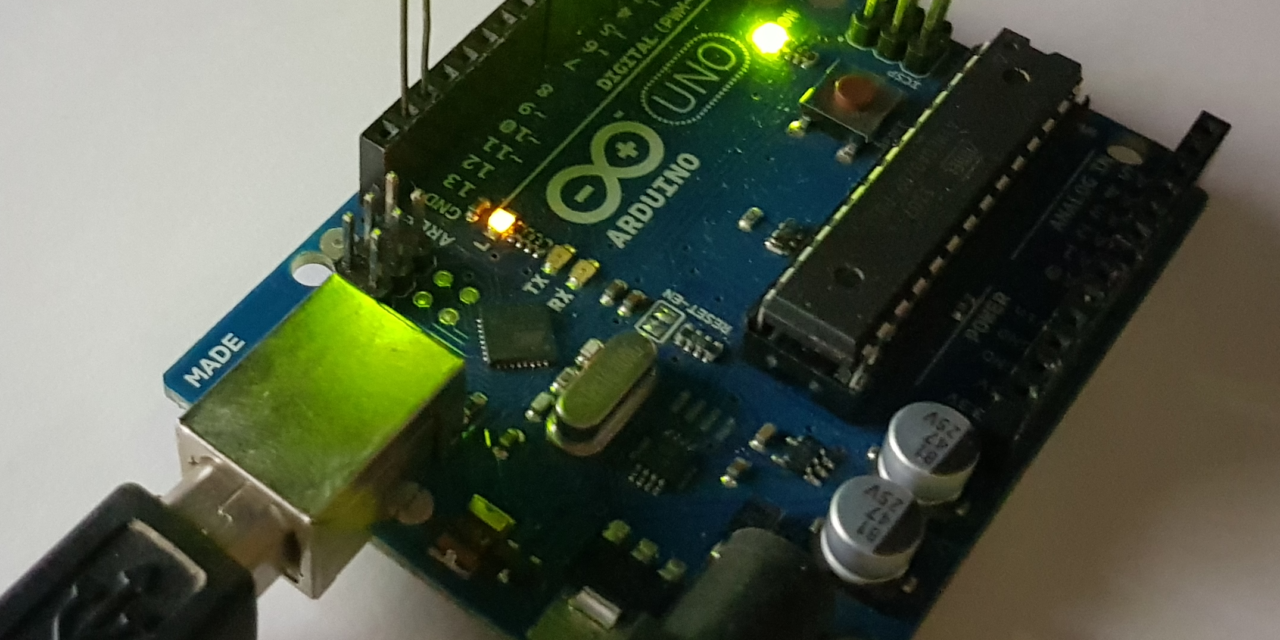
El LED de la placa Arduino se encenderá y apagará. De esta forma habremos verificado que la conexión funciona correctamente:
La ventaja de usar este tipo de conexión es que podremos manipular la placa Arduino desde un equipo informático. Esto nos permitirá realizar cualquier acción según cualquier evento que queramos controlar. Por ejemplo, usando el encendido del LED, podríamos encender el LED durante unos segundos cuando llegue un correo electrónico (o cualquier otra cosa).
Anexo
Código Arduino Firmata para preparar controlador Arduino UNO para conexión USB:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 |
/* Firmata is a generic protocol for communicating with microcontrollers from software on a host computer. It is intended to work with any host computer software package. To download a host software package, please click on the following link to open the list of Firmata client libraries in your default browser. https://github.com/firmata/arduino#firmata-client-libraries Copyright (C) 2006-2008 Hans-Christoph Steiner. All rights reserved. Copyright (C) 2010-2011 Paul Stoffregen. All rights reserved. Copyright (C) 2009 Shigeru Kobayashi. All rights reserved. Copyright (C) 2009-2016 Jeff Hoefs. All rights reserved. This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. See file LICENSE.txt for further informations on licensing terms. Last updated August 17th, 2017 */ #include <Servo.h> #include <Wire.h> #include <Firmata.h> #define I2C_WRITE B00000000 #define I2C_READ B00001000 #define I2C_READ_CONTINUOUSLY B00010000 #define I2C_STOP_READING B00011000 #define I2C_READ_WRITE_MODE_MASK B00011000 #define I2C_10BIT_ADDRESS_MODE_MASK B00100000 #define I2C_END_TX_MASK B01000000 #define I2C_STOP_TX 1 #define I2C_RESTART_TX 0 #define I2C_MAX_QUERIES 8 #define I2C_REGISTER_NOT_SPECIFIED -1 // the minimum interval for sampling analog input #define MINIMUM_SAMPLING_INTERVAL 1 /*============================================================================== * GLOBAL VARIABLES *============================================================================*/ #ifdef FIRMATA_SERIAL_FEATURE SerialFirmata serialFeature; #endif /* analog inputs */ int analogInputsToReport = 0; // bitwise array to store pin reporting /* digital input ports */ byte reportPINs[TOTAL_PORTS]; // 1 = report this port, 0 = silence byte previousPINs[TOTAL_PORTS]; // previous 8 bits sent /* pins configuration */ byte portConfigInputs[TOTAL_PORTS]; // each bit: 1 = pin in INPUT, 0 = anything else /* timer variables */ unsigned long currentMillis; // store the current value from millis() unsigned long previousMillis; // for comparison with currentMillis unsigned int samplingInterval = 19; // how often to run the main loop (in ms) /* i2c data */ struct i2c_device_info { byte addr; int reg; byte bytes; byte stopTX; }; /* for i2c read continuous more */ i2c_device_info query[I2C_MAX_QUERIES]; byte i2cRxData[64]; boolean isI2CEnabled = false; signed char queryIndex = -1; // default delay time between i2c read request and Wire.requestFrom() unsigned int i2cReadDelayTime = 0; Servo servos[MAX_SERVOS]; byte servoPinMap[TOTAL_PINS]; byte detachedServos[MAX_SERVOS]; byte detachedServoCount = 0; byte servoCount = 0; boolean isResetting = false; // Forward declare a few functions to avoid compiler errors with older versions // of the Arduino IDE. void setPinModeCallback(byte, int); void reportAnalogCallback(byte analogPin, int value); void sysexCallback(byte, byte, byte*); /* utility functions */ void wireWrite(byte data) { #if ARDUINO >= 100 Wire.write((byte)data); #else Wire.send(data); #endif } byte wireRead(void) { #if ARDUINO >= 100 return Wire.read(); #else return Wire.receive(); #endif } /*============================================================================== * FUNCTIONS *============================================================================*/ void attachServo(byte pin, int minPulse, int maxPulse) { if (servoCount < MAX_SERVOS) { // reuse indexes of detached servos until all have been reallocated if (detachedServoCount > 0) { servoPinMap[pin] = detachedServos[detachedServoCount - 1]; if (detachedServoCount > 0) detachedServoCount--; } else { servoPinMap[pin] = servoCount; servoCount++; } if (minPulse > 0 && maxPulse > 0) { servos[servoPinMap[pin]].attach(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), minPulse, maxPulse); } else { servos[servoPinMap[pin]].attach(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin)); } } else { Firmata.sendString("Max servos attached"); } } void detachServo(byte pin) { servos[servoPinMap[pin]].detach(); // if we're detaching the last servo, decrement the count // otherwise store the index of the detached servo if (servoPinMap[pin] == servoCount && servoCount > 0) { servoCount--; } else if (servoCount > 0) { // keep track of detached servos because we want to reuse their indexes // before incrementing the count of attached servos detachedServoCount++; detachedServos[detachedServoCount - 1] = servoPinMap[pin]; } servoPinMap[pin] = 255; } void enableI2CPins() { byte i; // is there a faster way to do this? would probaby require importing // Arduino.h to get SCL and SDA pins for (i = 0; i < TOTAL_PINS; i++) { if (IS_PIN_I2C(i)) { // mark pins as i2c so they are ignore in non i2c data requests setPinModeCallback(i, PIN_MODE_I2C); } } isI2CEnabled = true; Wire.begin(); } /* disable the i2c pins so they can be used for other functions */ void disableI2CPins() { isI2CEnabled = false; // disable read continuous mode for all devices queryIndex = -1; } void readAndReportData(byte address, int theRegister, byte numBytes, byte stopTX) { // allow I2C requests that don't require a register read // for example, some devices using an interrupt pin to signify new data available // do not always require the register read so upon interrupt you call Wire.requestFrom() if (theRegister != I2C_REGISTER_NOT_SPECIFIED) { Wire.beginTransmission(address); wireWrite((byte)theRegister); Wire.endTransmission(stopTX); // default = true // do not set a value of 0 if (i2cReadDelayTime > 0) { // delay is necessary for some devices such as WiiNunchuck delayMicroseconds(i2cReadDelayTime); } } else { theRegister = 0; // fill the register with a dummy value } Wire.requestFrom(address, numBytes); // all bytes are returned in requestFrom // check to be sure correct number of bytes were returned by slave if (numBytes < Wire.available()) { Firmata.sendString("I2C: Too many bytes received"); } else if (numBytes > Wire.available()) { Firmata.sendString("I2C: Too few bytes received"); } i2cRxData[0] = address; i2cRxData[1] = theRegister; for (int i = 0; i < numBytes && Wire.available(); i++) { i2cRxData[2 + i] = wireRead(); } // send slave address, register and received bytes Firmata.sendSysex(SYSEX_I2C_REPLY, numBytes + 2, i2cRxData); } void outputPort(byte portNumber, byte portValue, byte forceSend) { // pins not configured as INPUT are cleared to zeros portValue = portValue & portConfigInputs[portNumber]; // only send if the value is different than previously sent if (forceSend || previousPINs[portNumber] != portValue) { Firmata.sendDigitalPort(portNumber, portValue); previousPINs[portNumber] = portValue; } } /* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- * check all the active digital inputs for change of state, then add any events * to the Serial output queue using Serial.print() */ void checkDigitalInputs(void) { /* Using non-looping code allows constants to be given to readPort(). * The compiler will apply substantial optimizations if the inputs * to readPort() are compile-time constants. */ if (TOTAL_PORTS > 0 && reportPINs[0]) outputPort(0, readPort(0, portConfigInputs[0]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 1 && reportPINs[1]) outputPort(1, readPort(1, portConfigInputs[1]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 2 && reportPINs[2]) outputPort(2, readPort(2, portConfigInputs[2]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 3 && reportPINs[3]) outputPort(3, readPort(3, portConfigInputs[3]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 4 && reportPINs[4]) outputPort(4, readPort(4, portConfigInputs[4]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 5 && reportPINs[5]) outputPort(5, readPort(5, portConfigInputs[5]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 6 && reportPINs[6]) outputPort(6, readPort(6, portConfigInputs[6]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 7 && reportPINs[7]) outputPort(7, readPort(7, portConfigInputs[7]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 8 && reportPINs[8]) outputPort(8, readPort(8, portConfigInputs[8]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 9 && reportPINs[9]) outputPort(9, readPort(9, portConfigInputs[9]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 10 && reportPINs[10]) outputPort(10, readPort(10, portConfigInputs[10]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 11 && reportPINs[11]) outputPort(11, readPort(11, portConfigInputs[11]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 12 && reportPINs[12]) outputPort(12, readPort(12, portConfigInputs[12]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 13 && reportPINs[13]) outputPort(13, readPort(13, portConfigInputs[13]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 14 && reportPINs[14]) outputPort(14, readPort(14, portConfigInputs[14]), false); if (TOTAL_PORTS > 15 && reportPINs[15]) outputPort(15, readPort(15, portConfigInputs[15]), false); } // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- /* sets the pin mode to the correct state and sets the relevant bits in the * two bit-arrays that track Digital I/O and PWM status */ void setPinModeCallback(byte pin, int mode) { if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == PIN_MODE_IGNORE) return; if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == PIN_MODE_I2C && isI2CEnabled && mode != PIN_MODE_I2C) { // disable i2c so pins can be used for other functions // the following if statements should reconfigure the pins properly disableI2CPins(); } if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin) && mode != PIN_MODE_SERVO) { if (servoPinMap[pin] < MAX_SERVOS && servos[servoPinMap[pin]].attached()) { detachServo(pin); } } if (IS_PIN_ANALOG(pin)) { reportAnalogCallback(PIN_TO_ANALOG(pin), mode == PIN_MODE_ANALOG ? 1 : 0); // turn on/off reporting } if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { if (mode == INPUT || mode == PIN_MODE_PULLUP) { portConfigInputs[pin / 8] |= (1 << (pin & 7)); } else { portConfigInputs[pin / 8] &= ~(1 << (pin & 7)); } } Firmata.setPinState(pin, 0); switch (mode) { case PIN_MODE_ANALOG: if (IS_PIN_ANALOG(pin)) { if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { pinMode(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), INPUT); // disable output driver #if ARDUINO <= 100 // deprecated since Arduino 1.0.1 - TODO: drop support in Firmata 2.6 digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), LOW); // disable internal pull-ups #endif } Firmata.setPinMode(pin, PIN_MODE_ANALOG); } break; case INPUT: if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { pinMode(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), INPUT); // disable output driver #if ARDUINO <= 100 // deprecated since Arduino 1.0.1 - TODO: drop support in Firmata 2.6 digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), LOW); // disable internal pull-ups #endif Firmata.setPinMode(pin, INPUT); } break; case PIN_MODE_PULLUP: if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { pinMode(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), INPUT_PULLUP); Firmata.setPinMode(pin, PIN_MODE_PULLUP); Firmata.setPinState(pin, 1); } break; case OUTPUT: if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == PIN_MODE_PWM) { // Disable PWM if pin mode was previously set to PWM. digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), LOW); } pinMode(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), OUTPUT); Firmata.setPinMode(pin, OUTPUT); } break; case PIN_MODE_PWM: if (IS_PIN_PWM(pin)) { pinMode(PIN_TO_PWM(pin), OUTPUT); analogWrite(PIN_TO_PWM(pin), 0); Firmata.setPinMode(pin, PIN_MODE_PWM); } break; case PIN_MODE_SERVO: if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { Firmata.setPinMode(pin, PIN_MODE_SERVO); if (servoPinMap[pin] == 255 || !servos[servoPinMap[pin]].attached()) { // pass -1 for min and max pulse values to use default values set // by Servo library attachServo(pin, -1, -1); } } break; case PIN_MODE_I2C: if (IS_PIN_I2C(pin)) { // mark the pin as i2c // the user must call I2C_CONFIG to enable I2C for a device Firmata.setPinMode(pin, PIN_MODE_I2C); } break; case PIN_MODE_SERIAL: #ifdef FIRMATA_SERIAL_FEATURE serialFeature.handlePinMode(pin, PIN_MODE_SERIAL); #endif break; default: Firmata.sendString("Unknown pin mode"); // TODO: put error msgs in EEPROM } // TODO: save status to EEPROM here, if changed } /* * Sets the value of an individual pin. Useful if you want to set a pin value but * are not tracking the digital port state. * Can only be used on pins configured as OUTPUT. * Cannot be used to enable pull-ups on Digital INPUT pins. */ void setPinValueCallback(byte pin, int value) { if (pin < TOTAL_PINS && IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == OUTPUT) { Firmata.setPinState(pin, value); digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin), value); } } } void analogWriteCallback(byte pin, int value) { if (pin < TOTAL_PINS) { switch (Firmata.getPinMode(pin)) { case PIN_MODE_SERVO: if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) servos[servoPinMap[pin]].write(value); Firmata.setPinState(pin, value); break; case PIN_MODE_PWM: if (IS_PIN_PWM(pin)) analogWrite(PIN_TO_PWM(pin), value); Firmata.setPinState(pin, value); break; } } } void digitalWriteCallback(byte port, int value) { byte pin, lastPin, pinValue, mask = 1, pinWriteMask = 0; if (port < TOTAL_PORTS) { // create a mask of the pins on this port that are writable. lastPin = port * 8 + 8; if (lastPin > TOTAL_PINS) lastPin = TOTAL_PINS; for (pin = port * 8; pin < lastPin; pin++) { // do not disturb non-digital pins (eg, Rx & Tx) if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { // do not touch pins in PWM, ANALOG, SERVO or other modes if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == OUTPUT || Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == INPUT) { pinValue = ((byte)value & mask) ? 1 : 0; if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == OUTPUT) { pinWriteMask |= mask; } else if (Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == INPUT && pinValue == 1 && Firmata.getPinState(pin) != 1) { // only handle INPUT here for backwards compatibility #if ARDUINO > 100 pinMode(pin, INPUT_PULLUP); #else // only write to the INPUT pin to enable pullups if Arduino v1.0.0 or earlier pinWriteMask |= mask; #endif } Firmata.setPinState(pin, pinValue); } } mask = mask << 1; } writePort(port, (byte)value, pinWriteMask); } } // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- /* sets bits in a bit array (int) to toggle the reporting of the analogIns */ //void FirmataClass::setAnalogPinReporting(byte pin, byte state) { //} void reportAnalogCallback(byte analogPin, int value) { if (analogPin < TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS) { if (value == 0) { analogInputsToReport = analogInputsToReport & ~ (1 << analogPin); } else { analogInputsToReport = analogInputsToReport | (1 << analogPin); // prevent during system reset or all analog pin values will be reported // which may report noise for unconnected analog pins if (!isResetting) { // Send pin value immediately. This is helpful when connected via // ethernet, wi-fi or bluetooth so pin states can be known upon // reconnecting. Firmata.sendAnalog(analogPin, analogRead(analogPin)); } } } // TODO: save status to EEPROM here, if changed } void reportDigitalCallback(byte port, int value) { if (port < TOTAL_PORTS) { reportPINs[port] = (byte)value; // Send port value immediately. This is helpful when connected via // ethernet, wi-fi or bluetooth so pin states can be known upon // reconnecting. if (value) outputPort(port, readPort(port, portConfigInputs[port]), true); } // do not disable analog reporting on these 8 pins, to allow some // pins used for digital, others analog. Instead, allow both types // of reporting to be enabled, but check if the pin is configured // as analog when sampling the analog inputs. Likewise, while // scanning digital pins, portConfigInputs will mask off values from any // pins configured as analog } /*============================================================================== * SYSEX-BASED commands *============================================================================*/ void sysexCallback(byte command, byte argc, byte *argv) { byte mode; byte stopTX; byte slaveAddress; byte data; int slaveRegister; unsigned int delayTime; switch (command) { case I2C_REQUEST: mode = argv[1] & I2C_READ_WRITE_MODE_MASK; if (argv[1] & I2C_10BIT_ADDRESS_MODE_MASK) { Firmata.sendString("10-bit addressing not supported"); return; } else { slaveAddress = argv[0]; } // need to invert the logic here since 0 will be default for client // libraries that have not updated to add support for restart tx if (argv[1] & I2C_END_TX_MASK) { stopTX = I2C_RESTART_TX; } else { stopTX = I2C_STOP_TX; // default } switch (mode) { case I2C_WRITE: Wire.beginTransmission(slaveAddress); for (byte i = 2; i < argc; i += 2) { data = argv[i] + (argv[i + 1] << 7); wireWrite(data); } Wire.endTransmission(); delayMicroseconds(70); break; case I2C_READ: if (argc == 6) { // a slave register is specified slaveRegister = argv[2] + (argv[3] << 7); data = argv[4] + (argv[5] << 7); // bytes to read } else { // a slave register is NOT specified slaveRegister = I2C_REGISTER_NOT_SPECIFIED; data = argv[2] + (argv[3] << 7); // bytes to read } readAndReportData(slaveAddress, (int)slaveRegister, data, stopTX); break; case I2C_READ_CONTINUOUSLY: if ((queryIndex + 1) >= I2C_MAX_QUERIES) { // too many queries, just ignore Firmata.sendString("too many queries"); break; } if (argc == 6) { // a slave register is specified slaveRegister = argv[2] + (argv[3] << 7); data = argv[4] + (argv[5] << 7); // bytes to read } else { // a slave register is NOT specified slaveRegister = (int)I2C_REGISTER_NOT_SPECIFIED; data = argv[2] + (argv[3] << 7); // bytes to read } queryIndex++; query[queryIndex].addr = slaveAddress; query[queryIndex].reg = slaveRegister; query[queryIndex].bytes = data; query[queryIndex].stopTX = stopTX; break; case I2C_STOP_READING: byte queryIndexToSkip; // if read continuous mode is enabled for only 1 i2c device, disable // read continuous reporting for that device if (queryIndex <= 0) { queryIndex = -1; } else { queryIndexToSkip = 0; // if read continuous mode is enabled for multiple devices, // determine which device to stop reading and remove it's data from // the array, shifiting other array data to fill the space for (byte i = 0; i < queryIndex + 1; i++) { if (query[i].addr == slaveAddress) { queryIndexToSkip = i; break; } } for (byte i = queryIndexToSkip; i < queryIndex + 1; i++) { if (i < I2C_MAX_QUERIES) { query[i].addr = query[i + 1].addr; query[i].reg = query[i + 1].reg; query[i].bytes = query[i + 1].bytes; query[i].stopTX = query[i + 1].stopTX; } } queryIndex--; } break; default: break; } break; case I2C_CONFIG: delayTime = (argv[0] + (argv[1] << 7)); if (argc > 1 && delayTime > 0) { i2cReadDelayTime = delayTime; } if (!isI2CEnabled) { enableI2CPins(); } break; case SERVO_CONFIG: if (argc > 4) { // these vars are here for clarity, they'll optimized away by the compiler byte pin = argv[0]; int minPulse = argv[1] + (argv[2] << 7); int maxPulse = argv[3] + (argv[4] << 7); if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { if (servoPinMap[pin] < MAX_SERVOS && servos[servoPinMap[pin]].attached()) { detachServo(pin); } attachServo(pin, minPulse, maxPulse); setPinModeCallback(pin, PIN_MODE_SERVO); } } break; case SAMPLING_INTERVAL: if (argc > 1) { samplingInterval = argv[0] + (argv[1] << 7); if (samplingInterval < MINIMUM_SAMPLING_INTERVAL) { samplingInterval = MINIMUM_SAMPLING_INTERVAL; } } else { //Firmata.sendString("Not enough data"); } break; case EXTENDED_ANALOG: if (argc > 1) { int val = argv[1]; if (argc > 2) val |= (argv[2] << 7); if (argc > 3) val |= (argv[3] << 14); analogWriteCallback(argv[0], val); } break; case CAPABILITY_QUERY: Firmata.write(START_SYSEX); Firmata.write(CAPABILITY_RESPONSE); for (byte pin = 0; pin < TOTAL_PINS; pin++) { if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { Firmata.write((byte)INPUT); Firmata.write(1); Firmata.write((byte)PIN_MODE_PULLUP); Firmata.write(1); Firmata.write((byte)OUTPUT); Firmata.write(1); } if (IS_PIN_ANALOG(pin)) { Firmata.write(PIN_MODE_ANALOG); Firmata.write(10); // 10 = 10-bit resolution } if (IS_PIN_PWM(pin)) { Firmata.write(PIN_MODE_PWM); Firmata.write(DEFAULT_PWM_RESOLUTION); } if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin)) { Firmata.write(PIN_MODE_SERVO); Firmata.write(14); } if (IS_PIN_I2C(pin)) { Firmata.write(PIN_MODE_I2C); Firmata.write(1); // TODO: could assign a number to map to SCL or SDA } #ifdef FIRMATA_SERIAL_FEATURE serialFeature.handleCapability(pin); #endif Firmata.write(127); } Firmata.write(END_SYSEX); break; case PIN_STATE_QUERY: if (argc > 0) { byte pin = argv[0]; Firmata.write(START_SYSEX); Firmata.write(PIN_STATE_RESPONSE); Firmata.write(pin); if (pin < TOTAL_PINS) { Firmata.write(Firmata.getPinMode(pin)); Firmata.write((byte)Firmata.getPinState(pin) & 0x7F); if (Firmata.getPinState(pin) & 0xFF80) Firmata.write((byte)(Firmata.getPinState(pin) >> 7) & 0x7F); if (Firmata.getPinState(pin) & 0xC000) Firmata.write((byte)(Firmata.getPinState(pin) >> 14) & 0x7F); } Firmata.write(END_SYSEX); } break; case ANALOG_MAPPING_QUERY: Firmata.write(START_SYSEX); Firmata.write(ANALOG_MAPPING_RESPONSE); for (byte pin = 0; pin < TOTAL_PINS; pin++) { Firmata.write(IS_PIN_ANALOG(pin) ? PIN_TO_ANALOG(pin) : 127); } Firmata.write(END_SYSEX); break; case SERIAL_MESSAGE: #ifdef FIRMATA_SERIAL_FEATURE serialFeature.handleSysex(command, argc, argv); #endif break; } } /*============================================================================== * SETUP() *============================================================================*/ void systemResetCallback() { isResetting = true; // initialize a defalt state // TODO: option to load config from EEPROM instead of default #ifdef FIRMATA_SERIAL_FEATURE serialFeature.reset(); #endif if (isI2CEnabled) { disableI2CPins(); } for (byte i = 0; i < TOTAL_PORTS; i++) { reportPINs[i] = false; // by default, reporting off portConfigInputs[i] = 0; // until activated previousPINs[i] = 0; } for (byte i = 0; i < TOTAL_PINS; i++) { // pins with analog capability default to analog input // otherwise, pins default to digital output if (IS_PIN_ANALOG(i)) { // turns off pullup, configures everything setPinModeCallback(i, PIN_MODE_ANALOG); } else if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(i)) { // sets the output to 0, configures portConfigInputs setPinModeCallback(i, OUTPUT); } servoPinMap[i] = 255; } // by default, do not report any analog inputs analogInputsToReport = 0; detachedServoCount = 0; servoCount = 0; /* send digital inputs to set the initial state on the host computer, * since once in the loop(), this firmware will only send on change */ /* TODO: this can never execute, since no pins default to digital input but it will be needed when/if we support EEPROM stored config for (byte i=0; i < TOTAL_PORTS; i++) { outputPort(i, readPort(i, portConfigInputs[i]), true); } */ isResetting = false; } void setup() { Firmata.setFirmwareVersion(FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_MAJOR_VERSION, FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_MINOR_VERSION); Firmata.attach(ANALOG_MESSAGE, analogWriteCallback); Firmata.attach(DIGITAL_MESSAGE, digitalWriteCallback); Firmata.attach(REPORT_ANALOG, reportAnalogCallback); Firmata.attach(REPORT_DIGITAL, reportDigitalCallback); Firmata.attach(SET_PIN_MODE, setPinModeCallback); Firmata.attach(SET_DIGITAL_PIN_VALUE, setPinValueCallback); Firmata.attach(START_SYSEX, sysexCallback); Firmata.attach(SYSTEM_RESET, systemResetCallback); // to use a port other than Serial, such as Serial1 on an Arduino Leonardo or Mega, // Call begin(baud) on the alternate serial port and pass it to Firmata to begin like this: // Serial1.begin(57600); // Firmata.begin(Serial1); // However do not do this if you are using SERIAL_MESSAGE Firmata.begin(57600); while (!Serial) { ; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for ATmega32u4-based boards and Arduino 101 } systemResetCallback(); // reset to default config } /*============================================================================== * LOOP() *============================================================================*/ void loop() { byte pin, analogPin; /* DIGITALREAD - as fast as possible, check for changes and output them to the * FTDI buffer using Serial.print() */ checkDigitalInputs(); /* STREAMREAD - processing incoming messagse as soon as possible, while still * checking digital inputs. */ while (Firmata.available()) Firmata.processInput(); // TODO - ensure that Stream buffer doesn't go over 60 bytes currentMillis = millis(); if (currentMillis - previousMillis > samplingInterval) { previousMillis += samplingInterval; /* ANALOGREAD - do all analogReads() at the configured sampling interval */ for (pin = 0; pin < TOTAL_PINS; pin++) { if (IS_PIN_ANALOG(pin) && Firmata.getPinMode(pin) == PIN_MODE_ANALOG) { analogPin = PIN_TO_ANALOG(pin); if (analogInputsToReport & (1 << analogPin)) { Firmata.sendAnalog(analogPin, analogRead(analogPin)); } } } // report i2c data for all device with read continuous mode enabled if (queryIndex > -1) { for (byte i = 0; i < queryIndex + 1; i++) { readAndReportData(query[i].addr, query[i].reg, query[i].bytes, query[i].stopTX); } } } #ifdef FIRMATA_SERIAL_FEATURE serialFeature.update(); #endif } |